publications, Réseau
Molecular Junctions for Terahertz Switches and Detectors
Molecular electronics targets tiny devices exploiting the electronic properties of the molecular orbitals, which can be tailored and controlled by the chemical structure and configuration of the molecules. Many functional devices have been experimentally demonstrated; however, these devices were operated in the low-frequency domain (mainly dc to MHz). This represents a serious limitation for electronic… Read More
publications, Réseau
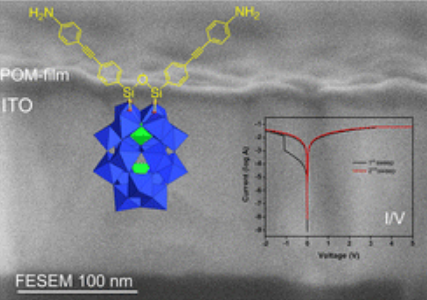
Covalent shaping of polyoxometalate molecular films onto ITO electrodes for charge trapping induced resistive switching
As nano-sized molecular oxides, polyoxometalates (POMs) hold great promise in non-volatile memory materials based on redox-active molecules. Materials processed from solution, by drop-casting, by embedding POMs in polymers, or using layer-by-layer deposition techniques have thus been reported and successfully investigated. Almost all of these examples are electrostatically assembled materials. We herein propose an original route… Read More
publications, Réseau
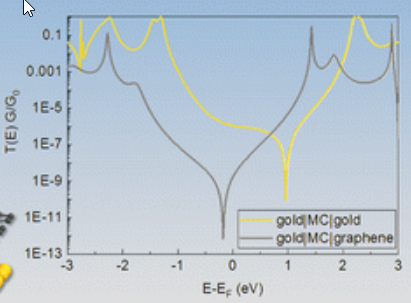
Destructive quantum interference in meta-oligo(phenyleneethynylene) molecular wires with gold–graphene heterojunctions
Quantum interference (QI) is well recognised as a significant contributing factor to the magnitude of molecular conductance values in both single-molecule and large area junctions. Numerous structure–property relationship studies have shown that para-connected oligo(phenyleneethynylene) (OPE) based molecular wires exemplify the impact of constructive quantum interference (CQI), whilst destructive quantum interference (DQI) effects are responsible for the… Read More
publications, Réseau
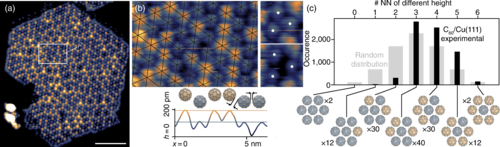
Geometrical Frustration, Correlated Disorder, and Emerging Order in a Corrugated C60 Monolayer
Under certain experimental conditions, the deposition of C60 molecules onto an atomically flat copper surface gives rise to the formation of corrugated islands. This corrugation, which reflects a molecular displacement perpendicular to the surface plane, presents an astonishing pattern: It is well described by a frustrated Ising spin Hamiltonian whose thermodynamics is compatible with a… Read More
publications, Réseau
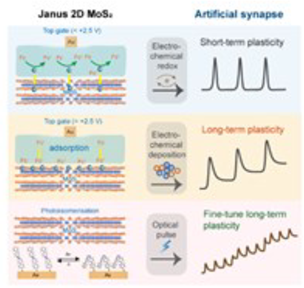
Opto-electrochemical Synaptic Memory in Supramolecularly Engineered Janus 2d MoS2
Artificial synapses combining multiple yet independent signal processing strategies in a single device are key enabler to achieve high-density of integration, energy efficiency and fast data manipulation in brain-like computing. By taming functional complexity, the use of hybrids comprising multiple materials as active components in synaptic devices represents a powerful route to encode both short-term… Read More
publications, Réseau
Enhanced interfacial water dissociation on a hydrated iron porphyrin single-atom catalyst in graphene
Single Atom Catalysis (SAC) is an expanding field of heterogeneous catalysis in which single metallic atoms embedded in different materials catalyze a chemical reaction, but these new catalytic materials still lack fundamental understanding when used in electrochemical environments. Recent characterizations of non-noble metals like Fe deposited on N-doped graphitic materials have evidenced two types of… Read More
publications, Réseau
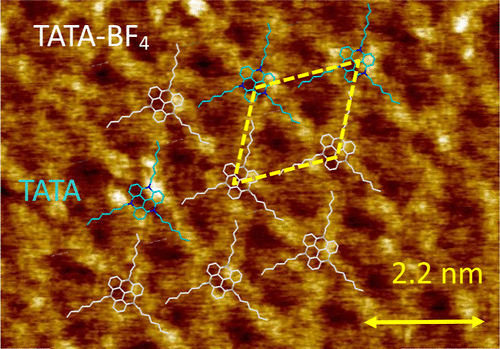
Nonuniform STM Contrast of Self-Assembled Tri-n-octyl-triazatriangulenium Tetrafluoroborate on HOPG
We have assembled 4,8,12-tri-n-octyl-4,8,12-triazatrianguleniumtetrafluoroborate (TATA-BF4) on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) and have studied the structure and tunneling properties of this self-assembled monolayer (SAM) using scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) under ambient conditions. We show that the triazatriangulenium cations TATA(+) form hexagonally packed structures driven by the interaction between the aromatic core and the HOPG lattice,… Read More
publications, Réseau
Quantum Transport in Large-Scale Patterned Nitrogen-Doped Graphene
It has recently been demonstrated how the nitrogen dopant concentration in graphene can be controlled spatially on the nano-meter scale using a molecular mask. This technique may be used to create ballistic electron optics-like structures of high/low doping regions; for example, to focus electron beams, harnessing the quantum wave nature of the electronic propagation. Here,… Read More
publications, Réseau
Elucidating the effect of spin crossover materials on graphene sensing devices
Graphene films are used to detect the presence and transition of spin crossover nanoparticle aggregates. Experiments performed far from the graphene neutrality point, combining impedance spectroscopy and Hall measurements, provide better insight into the mechanism for the change of impedance of the graphene layer in proximity with different states of the molecular structure. We observe… Read More
publications, Réseau
A simple and efficient process for the synthesis of 2D carbon nitrides and related materials
We describe here a new process for the synthesis of very high quality 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs), such a C2N and CN carbon nitrides. This process relies on the use of a metallic surface as both a reagent and a support for the coupling of small halogenated building blocks. The conditions of the assembly… Read More